Glycation is the reaction that occurs between sugars and other molecules within our bodies. The dreaded ‘sugar sag’ is just one example of its detrimental activities and cutting edge research has connected glycation to impaired barrier function, pigmentation, acne and increased oxidative stress in the skin.
Uk diets have higher levels of sugar than ever before, in fact most people in the uk consume on average 3 times more sugar than the recommended daily amount.
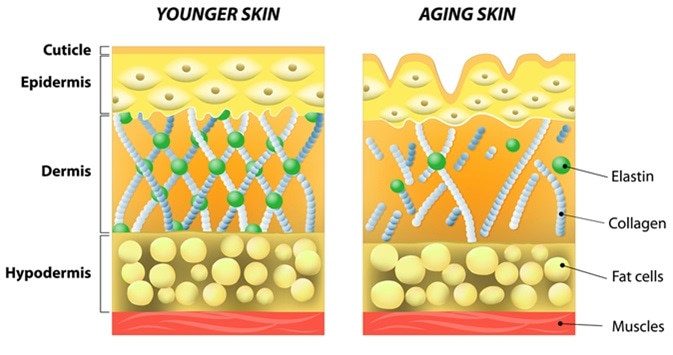
Glycation is a reaction that occurs when sugar molecules bond with protein molecules to form a new differently shaped particle. These molecules then go on to change the structural elements in the skin, for instance long chains of collagen proteins that make up the scaffolding of the skin and hold the skin upright are disrupted. Glycation changes the shape of the collagen molecule, it becomes stiffer and more prone to snapping. When this snapping happens and the skin no longer has no solid structure holding it up, we notice wrinkles and sagging skin as well as poor wound healing.
Glycation also alters the amount of lipids in the skin cells, this causes an imbalance in the skins fatty acids, ceremides and good cholesterol and can cause a weakened, compromised skin barrier, leading to TEWL (Trans Eptdermal Water Loss), meaning skin will likely become more dry, dehydrated and sensitive.
Gylcation has also been shown to increase rates of pigmentation and hyperpigmentation, Rosacea and Acne.
The detrimental impact of glycation on the skin means targeted support is necessary. Certain ingredients are thought to improve the rate and quality of the collagen we create.
Vitamin A is widely known for its beneficial action on the skin. It helps to create a foundation for healthy skin. Omega Fatty acids and antioxidants are also thought to increase the rate of collagen production.
Vitamin C is essential for collagen production, as it is a co-factor for several of the enzymes critical in its production, Without Vitamin C in the body, collagen could not be created. Vitamin C stimulates at least four genes related to collagen, a deficiency in vitamin C tends to cause the skin to loose strength, wrinkle and sag. One study has shown Vitamin C inhibits the process of glycation by 73%.
Alongside Vitamin C ingredients such as MSM and SOD are also involved in the synthesis of collagen. And topically AHA’s and BHA’s have a beneficial impact helping to stimulate cell turnover and collagen production. Other ingredients vital to collagen production include amino acids, Zinc and Vitamin B6 – So ensuring a balanced, comprehensive nutrient intake is vital to maintain healthy skin and collagen production.
Research has shown Green tea consistently lowers glycation in the skin, research has also shown that 2 months of topical and oral antioxidants can begin to reverse the impacts of glycation. Other beneficial antioxidants that assist on the reduction on oxidative stress on the sin include, lycopene, astaxanthin, beta-carotene and lutein.
Its always a good idea to use both to ensure we are getting the maximum amount of Vitamin A to the skin. Topical Vitamin A fortifies the skin from the outside, while oral Vitamin A feeds from the inside reaching the deepest layers off the skin, feeding the skin for 24 hours.